Single screw extrusion uses a single rotating screw, while twin screw extrusion relies on two intermeshing screws for enhanced mixing. This difference affects product quality and process control. For simple, high-volume production, a Single Plastic Screw Barrel suits most needs. Twin Screw Extruder Barrels and Twin Screws For Plastic Extruders excel in complex mixing.
Single Screw Extrusion Explained
How Single Screw Extrusion Works
Single screw extrusion uses a single rotating screw inside a heated barrel. The screw moves raw plastic or rubber material forward, where friction and heat melt it. The melted material passes through a die to form a continuous shape. Operators control key process parameters such as barrel temperature (usually 160–180 °C), screw speed, and die temperature. The take-up unit speed and water tank temperature help control the final product’s diameter and cooling. The screw performs three main functions: conveying, melting, and mixing. Barrel design features like hard tempering and chrome plating reduce friction and sticking, ensuring smooth operation.
Advantages of Single Screw Extrusion
Manufacturers choose single screw extrusion for its simplicity and cost-effectiveness. The design allows for easy operation and maintenance. Lower initial investment and operating costs make it attractive for many businesses. Energy efficiency stands out, as the system uses optimized heating and fewer moving parts. Operators can achieve consistent product quality by adjusting temperature, pressure, and screw speed. The system handles a wide range of raw materials, making it versatile for different production needs.
Tip: Regular maintenance and real-time energy monitoring can further improve efficiency and product quality.
Limitations of Single Screw Extrusion
Single screw extrusion faces some challenges. Throughput may become unstable at high screw speeds, limiting production rates. Maintaining melt temperature and product homogeneity can be difficult, especially with complex materials. The process may struggle with advanced mixing or formulations that require precise control. Feed behavior and throughput also depend heavily on screw design and feed opening geometry.
Typical Applications of Single Screw Extrusion
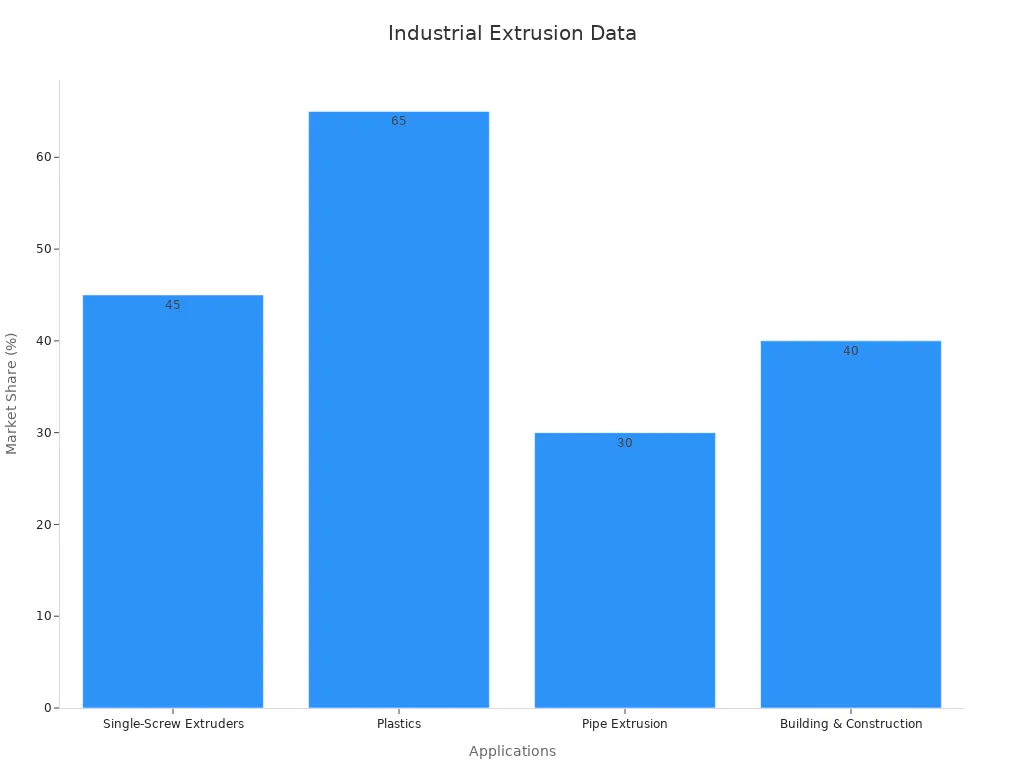
Single screw extrusion finds use in many industries. Packaging leads the market, with about 60% share, producing films and sheets from polymers like PE, PP, and PVC. The construction sector uses it for pipes and profiles, while automotive manufacturers rely on it for interior and exterior parts. Medical, consumer goods, and electronics industries also benefit from this technology.
| Model Type | Screw Diameter (mm) | L:D Ratio | Motor Power (kW) | Output Capacity (kg/hr) | Notes on Efficiency and Standards |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High Efficient Single Screw | 60 – 120 | 38:1 | 110 – 315 | 465 – 1300 | 20-30% higher rate; Siemens AC motors, CE-certified |
| Normal Standard Single Screw | 60 – 120 | 33:1 | 55 – 315 | 150 – 900 | Standard quality components |
Twin Screw Extrusion Overview
How Twin Screw Extrusion Works
Twin screw extrusion uses two intermeshing screws that rotate inside a heated barrel. Operators feed raw materials like pellets or powders into the hopper. The screws move the material forward, compressing and kneading it. Heat from the barrel and friction from the screws melt the material. Specialized screw elements mix and homogenize the melt, ensuring even dispersion of additives. The molten material then passes through a die to form the final product. Modular barrels with heating and cooling zones allow precise temperature control. Venting zones remove air and volatiles, improving product quality.
Strengths of Twin Screw Extrusion
Twin screw extrusion offers several advantages:
- Superior mixing and homogenization due to intermeshing screws.
- High shear forces improve blending and product uniformity.
- Modular design allows easy adjustment for different materials.
- Enhanced temperature control reduces thermal degradation.
- High throughput and productivity support large-scale manufacturing.
- Flexible screw configurations optimize processing for various polymers.
- Better process control with independent adjustment of screw speed and temperature.
- Longer equipment life as load is shared between two screws.
| Technical Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Superior Mixing & Homogenization | Intermeshing screws create shear and kneading effects for uniform mixing. |
| High Throughput & Productivity | Co-rotating screws enable higher production rates and efficiency. |
| Versatility | Capable of processing diverse polymers and complex formulations. |
Weaknesses of Twin Screw Extrusion
- Twin screw extruders have a complex structure and higher cost.
- The flow of material inside the extruder is difficult to model and predict.
- Pressure fluctuations can occur due to screw geometry.
- Monitoring particle size and process stability presents challenges.
- Scaling up from lab to production requires careful adjustment.
Common Uses for Twin Screw Extrusion
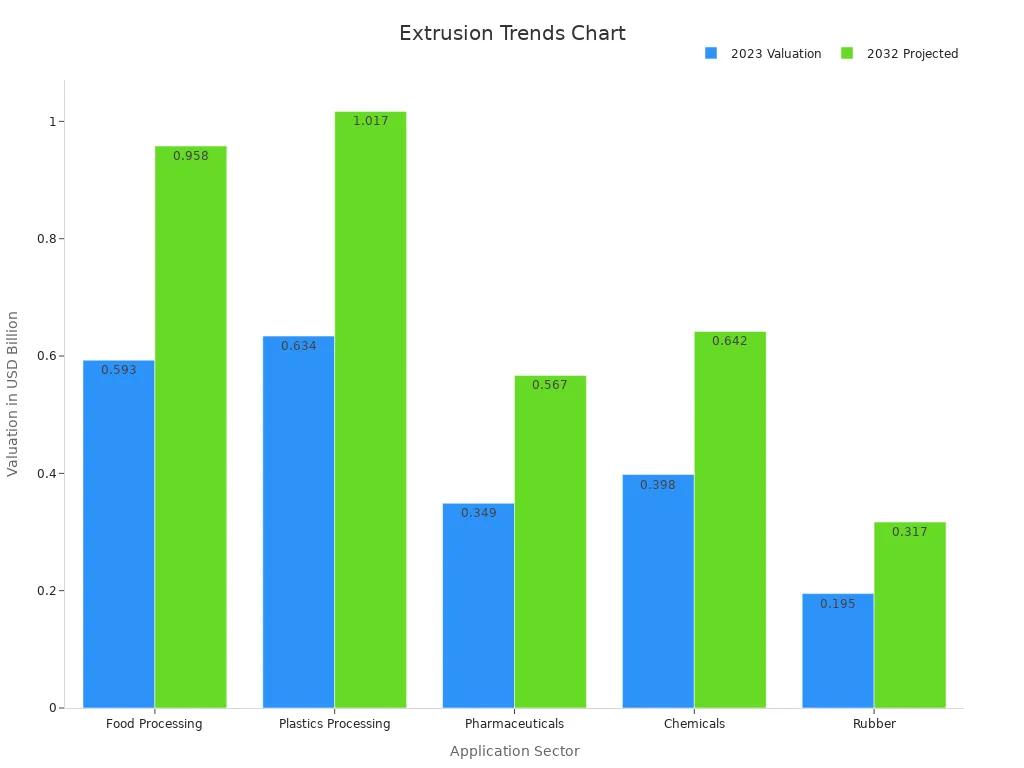
Twin screw extruders play a key role in many industries. Manufacturers use them for compounding plastics, processing recycled materials, and producing bioplastics. The food industry relies on them for snacks, cereals, and pet food. Pharmaceutical companies use twin screw extrusion for making solid dosage forms. Chemical and rubber sectors also benefit from their precise mixing and control. The market for twin screw extruders continues to grow, driven by demand in Asia-Pacific, Europe, and North America.
Single Screw Extrusion vs Twin Screw Extrusion: Key Comparisons

Design and Mechanism Differences
Single screw extrusion uses a single rotating screw with a simple helical pattern. This design pushes material forward through the barrel. In contrast, twin screw extruders feature two intermeshing screws. These screws can rotate in the same or opposite directions and often include kneading blocks for better mixing. The table below highlights the main technical differences:
| Aspect | Single Screw Extruder | Twin Screw Extruder |
|---|---|---|
| Screw Design | Single rotating screw with a simple helical pattern pushing material forward. | Two intermeshing screws, possibly co- or counter-rotating, with complex geometries including kneading blocks. |
| Mixing Capability | Suitable for homogeneous materials and simple mixing. | Superior mixing due to intermeshing screws, enabling better dispersion of additives and fillers. |
| Throughput & Output | Generally lower throughput and output rates. | Higher throughput and output, suitable for large-scale production. |
| Temperature Control | Basic control over temperature, screw speed, and barrel pressure. | Enhanced temperature regulation with internal heating/cooling zones along the barrel. |
| Material Handling | Effective for thermoplastics, elastomers, and recycled plastics with consistent product quality. | Better suited for high-viscosity, heat-sensitive, and complex formulations requiring precise control. |
| Process Flexibility | Less flexible, simpler operation and maintenance. | Greater flexibility due to modular screw design and adjustable parameters. |
| Degassing Capability | Limited degassing and devolatilization capabilities. | Effective degassing and devolatilization, important for quality control. |
| Application Examples | Plastic films, pipes, compounding, wire coating, sheet extrusion, food processing. | Polymer compounding, food processing, pharmaceuticals, and complex material processing. |
Researchers like Shen et al. and Sastrohartono et al. have shown that twin screw extruders offer more advanced design features, such as better shear flux and energy efficiency, especially for complex materials.
Mixing and Processing Capabilities
Mixing and processing capabilities set these two technologies apart. Single screw extrusion works well for simple, homogeneous materials. It can handle basic mixing tasks, but struggles with advanced blending or formulations that require precise control. Twin screw extruders excel in mixing. Their intermeshing screws create strong shear and kneading effects. This action ensures even dispersion of additives and fillers, which is critical for high-quality products. Operators can adjust screw elements and barrel zones to fine-tune the process for different materials. As a result, twin screw systems support complex recipes and demanding production requirements.
Note: For manufacturers who need to blend multiple polymers or add fillers, twin screw extruders provide a clear advantage in mixing performance.
Throughput and Efficiency
Throughput and efficiency play a major role in choosing between these systems. Single screw extrusion typically offers lower throughput, making it suitable for smaller production targets. It operates at slower processing speeds and delivers consistent results for standard products. Twin screw extruders, on the other hand, achieve higher throughput and faster processing speeds. They support large capacity requirements and maintain product quality even with complex granulation. The table below compares key metrics:
| Metric | Single Screw Extruder | Twin Screw Extruder |
|---|---|---|
| Throughput | Lower throughput, suitable for low production targets | Higher throughput, suitable for large capacity requirements |
| Processing Speed | Slower processing speeds | Faster processing speeds |
| Product Quality | Limited mixing intensity, less complex granulation | Enhanced mixing, supports complex granulation |
| Operational Costs | Lower operational costs due to simplicity and energy efficiency | Higher operational costs due to complexity and maintenance |
| Flexibility | Less flexible, simpler operation | Greater flexibility, can handle complex formulations |
| Output Rates | Generally lower output rates | Higher output rates |
Twin screw extruders often justify their higher operational costs with increased productivity and the ability to handle more challenging materials.
Flexibility and Versatility
Flexibility and versatility are essential for modern manufacturing. Single screw extrusion provides reliable performance for standard products and materials. However, it offers limited flexibility when switching between different formulations or product types. Twin screw extruders stand out in this area. At the K 2016 trade show, advanced twin screw lines demonstrated rapid changeovers between materials, colors, and thicknesses. Some systems switched formats in minutes, not hours. These extruders processed multi-layer films with up to 11 layers, handling materials like EVOH, nylon, and various polyethylene grades. Production data showed a 45.8% reduction in material waste and nearly 29% energy savings after upgrading to flexible twin screw systems. The return on investment period also shortened by over 26%. These improvements highlight the operational advantages of twin screw extruders in complex, multi-material environments.
Cost and Maintenance Considerations
Cost and maintenance influence the final decision for many manufacturers. Single screw extrusion systems cost less to purchase and operate. Their simple design means fewer parts to maintain and lower energy consumption. Routine maintenance is straightforward, and downtime remains minimal. Twin screw extruders require a higher initial investment. Their complex structure and advanced features lead to increased maintenance needs and higher energy use. However, for companies producing high-value or complex products, the benefits of flexibility, throughput, and quality often outweigh the extra costs. Choosing the right system depends on balancing these factors with production goals and budget.
Choosing the Right Extruder for Your Needs
Material Suitability
Selecting the right extruder starts with understanding material compatibility. Key machine components such as screw speed, diameter, and length-to-diameter ratio affect how well the extruder processes different materials. For example, higher L/D ratios help with complex materials that need thorough melting and mixing. Barrel design, including temperature zones and venting, supports sensitive or recycled materials. Industry guidelines recommend matching the extruder to the material’s processing temperature, viscosity, and flow rate. Single screw extrusion works well for mass processing of thermoplastics, while twin screw extruders handle complex formulations in food, pharmaceutical, and polymer industries.
Production Scale and Output
Production scale and output requirements play a major role in extruder selection. Higher output rates can increase energy use and maintenance needs. Modular screw configurations allow for better scalability and performance. Studies show that throughput and fill level impact product quality and mixing efficiency. Larger extruders require careful adjustment of operating parameters to maintain consistent results. Companies must balance production goals with operational costs and technical complexity.
Budget and Cost Factors
Cost considerations include both upfront and ongoing expenses. The table below outlines key cost factors:
| Cost Factor | Description | Budget Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Purchase | Varies by size and type | Major upfront investment |
| Certification | ISO 9001, CE, etc. | May increase purchase price |
| Maintenance | Regular servicing required | Ongoing annual fees |
| Energy Consumption | Efficient models save long-term costs | Higher upfront, lower monthly |
| Training | Needed for proper operation | 1-3% of purchase price |
Manufacturers in Asia-Pacific often benefit from lower operational costs due to regional advantages.
Application-Based Recommendations
When choosing an extrusion system, companies should consider production volume, supplier flexibility, and quality requirements. For basic products and small-scale runs, single screw extrusion offers simplicity and lower costs. Twin screw extruders suit high-volume, complex, or innovative products that require advanced mixing and flexibility. Industries such as automotive, food, and pharmaceuticals often prefer twin screw systems for their versatility and product quality. Companies aiming for market differentiation may switch to twin screw extrusion to achieve unique product features.
- Twin screw extruders use two screws for better mixing and stable material flow.
- They handle more material types and offer higher productivity.
- Single screw extrusion works best for simple, low-viscosity materials.
- For complex products or higher efficiency, companies should select twin screw extruders.
FAQ
What is the main difference between single screw and twin screw extrusion?
Single screw extrusion uses one screw for basic processing. Twin screw extrusion uses two screws for better mixing and handling of complex materials.
Which extruder works best for recycling plastics?
Twin screw extruders handle recycled plastics more efficiently. They provide better mixing and control, which improves product quality.
How does maintenance compare between the two types?
Single screw extruders require less maintenance. Twin screw extruders need more attention due to their complex design and additional parts.
Post time: Jul-08-2025
